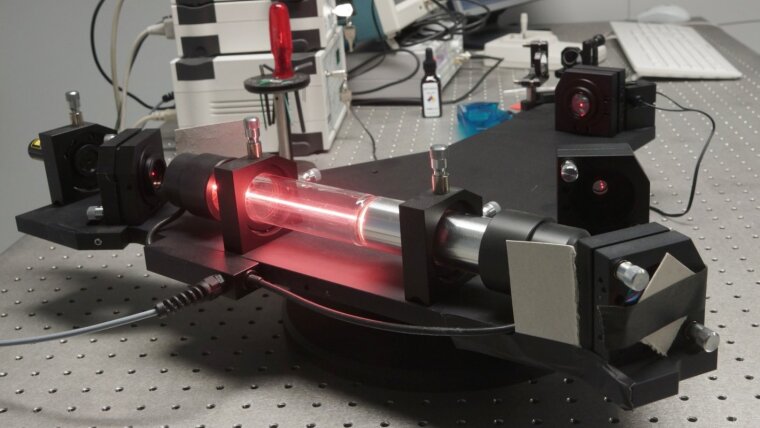
Laser gyroscopes are optical instruments for measuring the angular velocity based on the Sagnac effect. In combination with accelerometers, they form so-called inertial measurement units that allow position and direction estimation by the dead reckoning technique. Today,
this technique is most commonly used to navigate vessels, spacecraft, satellites and even aircraft. Versions with high accuracy and precision are also used to measure the earth's rotation without the need for astronomical observations. There are several advantages of this technology over conventional mechanical gyroscopes and GPS position estimation, such as:
- No communication with external devices is necessary (dead reckoning)
- It features digital output with a fast update rate
- It is insensitive to vibration (no moving parts)
The presented lab work demonstrates the operating principles of a laser gyroscope based on a HeNe-laser ring cavity. A complete setup mounted on a rotary table including alignment tools, detectors, and analysis electronics/software is provided for the lab work.
Further content and detailed descriptions are available to enrolled students via the course's page at the Moodle website of the Friedrich Schiller University Jena.